Advanced Cardiovascular Care Center Heart Clinic in Houston provides the highest standard of excellence in Cardiovascular Care while exemplifying our ideals of customized patient care. Our goal is that of achieving superior patient satisfaction in every aspect of services given. We perceive our organization as a team of cardiology doctors in Houston working towards one common goal, that of our patients’ good health and well being. To that end, we pledge our services.
Our Cardiac Care Center in Houston offers health services in a warm, comforting, relaxing atmosphere. The practice is committed to high quality patient care in an ever-changing health care environment.
Dr. Annie Varughese Cardiology Doctor in Houston attended the Medical College of Georgia, Augusta, Georgia and subsequently completed her residency in Internal Medicine as well as Fellowship in Cardiovascular Diseases at the University of Texas Medical School in Houston. Dr. Annie Varughese Houston Cardiologist pursued further training in Interventional Cardiology at The Texas Heart Institute/Baylor College of Medicine and now has been in private practice in the Northwest Houston and Woodlands area for the past 20 years.
The practice operates under the direction of Dr. Annie Varughese, Board-Certified one of Best Cardiologists in Houston and leading cardiology specialist providing treatment for heart attacks, angina, hypertension and all aspects of cardiology. We are well-trained staff of Heart Doctors in Houston offers a variety of comprehensive, state-of-the-art services to diagnose, treat and manage heart disease. Our Top Cardiologists in Houston improve the lives of thousands of patients every year using advanced surgical and non-surgical procedures.
Dr. Annie Varughese Heart Specialist in Houston is an avid speaker regarding issues in cardiology including that of Women & Heart Disease and holds the title of Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine at the University of Texas Medical School in Houston.
Signs of Heart Disease :-
Most heart attacks are indirectly caused by coronary artery disease or Atherosclerosis, a condition in which fatty deposits (plaque) build up on the walls of an artery. This narrows the arteries and restricts blood flow to the muscle of the heart. A heart attack is usually triggered by a tear or rupture of the plaque, which leads to the formation of a blood clot that blocks the blood flow in the artery. Spasm of the artery can also contribute to the blockage. The symptoms of a heart attack may be far more subtle in women than in men. Chest pain or discomfort is typically the most common symptom in men and women, common symptoms include
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe fatigue
- Dizziness, fainting
- Feelings of heartburn or indigestion in the upper abdomen
- Pain that radiates into the arms (on the left side more than the right)
- Pain high in the back, jaw, or neck
- Heart palpitations
- Profuse sweating
- Shortness of breath
- A fear of impending death
Nuclear Stress Test :-
Nuclear Stress Test used in medicine and cardiology to measure the heart’s ability to respond to external stress in a controlled clinical environment. The stress response is induced by exercise or drug stimulation. Nuclear stress tests compare the coronary circulation while the patient is at rest with the same patient’s circulation observed during maximum physical exertion, showing any abnormal blood flow to the heart’s muscle tissue. The results can be interpreted as a reflection on the general physical condition of the test patient. This test can be used to diagnose ischemic heart disease, and for patient prognosis after a heart attack.
Transesophageal ECHO :-
This is an alternative way to perform an echocardiogram. A specialized probe containing an ultrasound transducer at its tip is passed into the patient’s esophagus. This allows image and Doppler evaluation which can be recorded. Transesophageal echocardiograms are most often utilized when transthoracic images are suboptimal and when a more clear and precise image is needed for assessment. This test is performed in the presence of a cardiologist, registered nurse, and ultrasound technician.
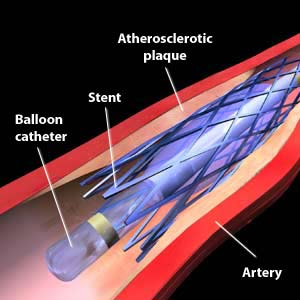
Cardiac Catheterization and Stenting :-
Cardiac Catheterization and Stenting is a minimally invasive procedure to access the coronary circulation and blood filled chambers of the heart using a catheter. It is performed for both diagnostic and interventional (treatment) purposes. Cardiac catheterization is a visually interpreted test performed to recognize occlusion, stenosis, restenosis, thrombosis or aneurysmal enlargement of the coronary artery lumens; heart chamber size; heart muscle contraction performance; and some aspects of heart valve function. Important internal heart and lung blood pressures, not measurable from outside the body, can be accurately measured during the test.
PFO & ASD Closure :-
PFO & ASD Closure is a form of congenital heart defect that enables blood flow between the left and right atria via the interatrial septum. The interatrial septum is the tissue that divides the right and left atria. Without this septum, or if there is a defect in this septum, it is possible for blood to travel from the left side of the heart to the right side of the heart, or vice versa. This results in the mixing of arterial and venous blood, which may or may not be clinically significant.
Advance Lipid Test :-
Advanced lipid testing can identify additional risk factors of coronary heart disease that standard blood-cholesterol tests typically do not. Advanced Lipid Testing can diagnose early diabetes, insulin resistance if you have a tendency towards clotting or if you are genetically prone to having a heart attack. We analyze your blood test results in combination with your family history, lifestyle, medications and existing clinical factors.
EKG Echocardiogram :-
It is an important part of the initial evaluation of a patient who is suspected to have a heart related problem. Small sticky electrodes are applied to the patient’s chest, arms and legs. However, with some systems, the electrodes may be applied to the chest, shoulders and the sides of the lower chest, or hips. Wires are used to connect the patient to an EKG machine. You will be asked to remain very still while a nurse or technician records the EKG. The electrical activity created by the patient’s heart is processed by the EKG machine and then printed on a special graph paper. This is then interpreted by your physician. It takes a few minutes to apply the EKG electrodes, and one minute to make the actual recording.
Echocardiography :-
An echocardiogram is a fairly common test that allows doctors to use sound waves to see the inside of one’s heart and see how it’s beating and pumping blood. This procedure can help identify various abnormalities in the heart muscle and valves. A doctor may suggest an echocardiogram if he or she suspects problems with the valves or chambers of the heart or the heart’s ability to pump. An echocardiogram can also be used to detect congenital heart defects in unborn babies.
Echocardiogram :-
Echocardiogram is a sonogram of the heart. Also known as a cardiac ultrasound, it uses standard ultrasound techniques to image two-dimensional slices of the heart.
Stress Echo :-
The stress echo test is done with heart stimulation, either by exercise on a treadmill with the patient connected to an electrocardiogram. People who cannot use their legs may exercise with a bicycle-like crank that you can turn with your arms. The level of mechanical stress is progressively increased by adjusting the difficulty (steepness of the slope) and speed. The test administrator or attending physician examines the symptoms and blood pressure response.
Holter-Event Monitor:-
A cardiac event monitor is a device used to monitor patients with transient cardiac symptoms.
Tilt Table :-
A tilt table test, occasionally called upright tilt testing is a medical procedure often used to diagnose dysautonomia or syncope. Patients with symptoms of dizziness or lightheadedness, with or without a loss of consciousness, suspected to be associated with a drop in blood pressure. The procedure tests for causes of syncope by attempting to cause syncope by having the patient lie flat on a special table or bed while connected to ECG and blood pressure monitors. The table then creates a change in posture from lying to standing.
External Counterpulsation Therapy :-
Enhanced External counterpulsation therapy is a procedure performed on individuals with angina or heart failure or cardiomyopathy in order to diminish their symptoms ischemia, improve functional capacity and quality of life. In various studies, EECP has been shown to relieve angina, and decrease the degree of ischemia in a cardiac stress test.
Peripheral Angiography and Stenting :-
Angiography is also commonly performed to identify vessel narrowing in patients with leg claudicating or cramps, caused by reduced blood flow down the legs and to the feet; in patients with renal stenosis and can be used in the head to find and repair stroke.
Carotid Stenting :-
Carotid artery stenting is an endovascular, catheter-based procedure which unblocks narrowing of the carotid artery lumen to prevent a stroke. Carotid artery stenosis can present with no symptoms or with symptoms such as transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) or cerebrovascular accidents (CVAs, strokes).
Carotid Ultrasound :-
Carotid Ultrasound is an ultrasound-based diagnostic imaging technique to reveal structural details of the carotid arteries, so as to look for blood clots, atherosclerotic plaque buildup, and other blood flow problems.
Cardiac MRI/Coronary CTA :-
Cardiac MRI/Coronary CTA – Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging is a medical imaging technology for the non-invasive assessment of the function and structure of the cardiovascular system. It is derived from and based on the same basic principles as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) but with optimization for use in the cardiovascular system.
Weight Loss Therapy :-
Weight Loss Therapy is a revolutionary fat burning product; providing the first scientific breakthrough in fat-loss in over 30 years. Containing natural, proprietary ingredients, Bios Life Slim helps your body naturally regulate the amount of fat stored. Drinking Bios Life Slim at least twice a day with your meals trains your body to burn away excess fat forever-without the jitters, hunger, or confusion of other weight-loss products or programs-creating a slimmer, more active, more attractive you.
Logon to www.advancedcardiodr.com and request an appointment for the desired service.